In his new book “The Anxious Generation“, Jonathan Haidt posits that the well-being of young people, and especially that of young girls, has decreased dramatically across the last fifteen years. The two major reasons for this decline, according to Haidt, are increased social media use and decreased play and interactions unsupervised by adults. In a nutshell, kids would be under-protected online and over-protected offline. Haidt goes on to suggest several solutions, such as smartphone bans in schools, increasing the age of social media use to 16, actually enforcing age limits, or increasing offline unregulated interactions (he co-started “Let Grow“).
Continue reading →Open-access publizieren: Green, gold oder diamond?
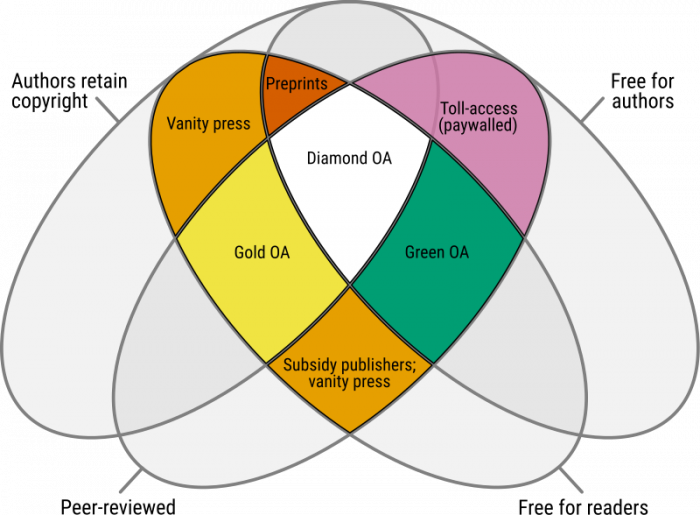
Open-access Publikationen in der Wissenschaft werden (erfreulicherweise) immer relevanter. Es gibt unterschiedliche Open-Access-Formate, und es ist schwer, hier den Überblick zu bewahren. Folgende Grafik, open-access publiziert auf Wikipedia, illustriert die unterschiedlichen Open-Access-Formate sehr gut.
Three observations on three years of Open Communication
The journey of open science and open research in the field of Communications started three years ago. The 2020 conference motto was Open Communication, and since then our community is engaging with questions on how best to implement open research practices into our field. Here are three observations!
Continue reading →Was sind Gefahren von sozialen Medien?
Häufig erhalte ich Presseanfragen zum Thema: Was sind Gefahren von sozialen Medien? Jüngst bekam ich eine E-Mail einer Schülerin, die mir für Ihre Seminararbeit hierzu neun konkrete Fragen gestellt hat, mit einem Fokus auf Kinder und Jugendliche. Mit ihrer Erlaubnis darf ich hier ihre Fragen und meine Antworten wiedergeben.
Continue reading →Diskriminiert Gendern?

Wie beeinflusst Gendern von journalistischen Artikeln die Textwahrnehmung und Aktivierung von Stereotypen? Diskriminiert Gendern? Und reduziert Gendern den Lesefluss? Frederieke Cirksena und Dominik Leiner untersuchten diese Frage in einem großen Online-Experiment – nun veröffentlicht in der Zeitschrift Studies in Communication and Media.
Continue reading →Teaching award for “Media Effects”

I’m incredibly proud that University of Vienna selected my lecture “Media Effects” for this year’s teaching award. It was awarded in the category “Promoting Activation and Course Completion”. And there was even a small ceremony during our summer fest — really cool!
Continue reading →Wie wirken Medien?
Wie wirken Medien? Diese Frage gehe ich in meiner Vorlesung “Rezeptions- und Wirkungsforschung” nach, die ich im Wintersemester 2021 an der Universität Wien gehalten habe.
Does the privacy paradox exist? Comment on Yu et al.’s (2020) meta-analysis
I was excited when last year I saw that International Journal of Information Management (IJIM) published a meta analysis on the privacy paradox. Does the privacy paradox exist? The authors concluded that yes, the “‘privacy paradox’ phenomenon [. . . ] exists in our research model”.
I was surprised, because this finding contradicts another meta-analysis by Baruh et al. (2017), which found significant relations between privacy concerns and information sharing. Also in my own research, I regularly find significant (though often small) effects (for example in this study).
Continue reading →Are people nowadays more happy?
Three years ago, I wrote a blog post on how happiness developed in Europe between 2002 and 2016. Using data from the European Social Survey, I analyzed self-reported levels of happiness, Internet use, social behavior, or health.
For a review I’m currently writing, I now updated these analyses with the (somewhat) new data for 2018 (2020 isn’t available yet). Overall, the data now include the responses of 430.870 (!) respondents.
Are people nowadays more happy than they used to be?
Continue reading →Open Science, Closed Doors?
When we published the Agenda for Open Science in Communication roughly one year ago, I expected to receive pushback. After all, we called for a sweeping change of several well-established research practices. Transparency instead of confidentiality, research openly accessible but not hidden behind paywalls, showing instead of telling, quality instead of quantity.
I expected to receive pushback coming from the established quantitative scholars. From the p-hackers, the grinders, the paper manufacturers, the data-dredgers, the beneficiaries of the old and closed system. However, I didn’t expect to receive pushback from the more qualitative-oriented scholars.1
Well, turns out I was wrong.
Continue reading →





